Peptides are small chains made from amino acids. Amino acids are the basic parts that build all proteins in our body. When two or more amino acids join together, they make a peptide. These chains are short; most are 2-50 amino acids long. They are smaller and simpler than full proteins, but they still do very important jobs.
Peptides help the body run many daily processes. They act as messengers, sending signals between cells. Some work as hormones. For example, insulin is a peptide that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Without peptides like this, the body would not stay balanced.
Over the past few years, scientists have increasingly focused on peptides. They are finding new ways to use them in medicine and science. Peptides can target specific cells or functions in the body, making them of interest to doctors and researchers. In this blog, we’ll talk about what peptides are, how they work, and what new research says about them.
What Are Peptides?
Peptides are short chains of amino acids connected by what’s called peptide bonds. When these chains get longer, they can turn into proteins. You can think of a peptide as a small version of a protein. It has fewer amino acids and is usually easier for the body to use or break down.
In the body, peptides act like tiny messengers. They help send signals between cells, control metabolism, support tissue growth, and help the immune system. Because they are small, they can move through the body quickly and act fast.
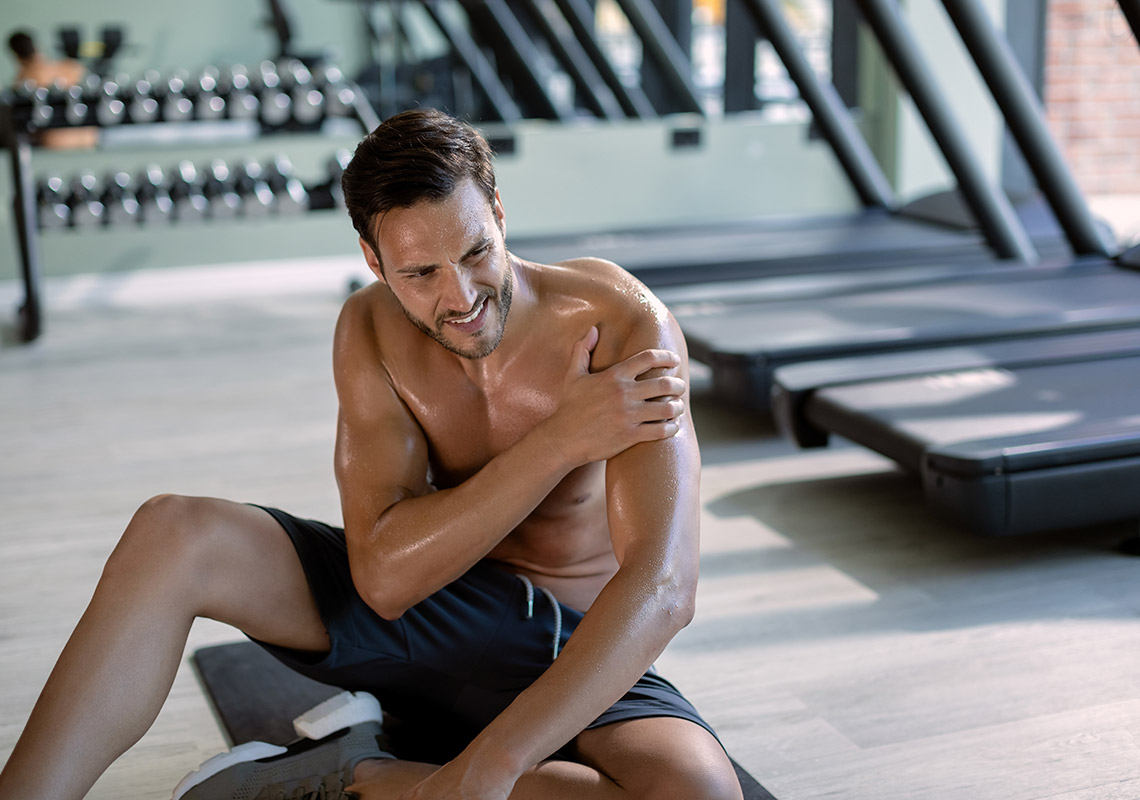
You might hear about peptides in skincare or fitness. Many creams use collagen peptides to help the skin look firm or smooth. In sports, some people use peptide supplements to help muscles grow or recover after training. But it’s important to remember that not all claims are proven. Real results depend on your health, diet, and how your body reacts.
How Peptides Work in the Body
Peptides work in the body by attaching to specific receptors on cell surfaces. Once they connect, they send signals that tell cells what to do, such as repair the tissue, reduce inflammation, or build proteins like collagen. Because of their targeted actions, peptides play a vital role in many body functions, from muscle repair to skin health. Here are the key ways peptides function in your body:
-
Receptor Binding
Peptides travel through the bloodstream and find the right cell receptor that matches them. When a peptide binds to its receptor, it triggers a change inside the cell.
-
Response Trigger
Once bound, the peptide activates a chain of events inside the cell. This can lead to actions like helping the cell take in glucose, divide, or produce collagen.
-
Building Proteins
Some peptides act as signals or building blocks for larger proteins that are essential for body structure and repair.
-
Tissue Repair and Inflammation Control
Peptides can signal cells to heal damaged tissue, reduce swelling, and improve blood flow to injured areas.
How Peptides Affect the Body
-
Muscle and Tissue Repair
Peptides stimulate collagen and IGF-1 production, helping repair muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
-
Growth Hormone Support
Certain peptides trigger the pituitary gland to release more HGH, promoting muscle growth and fat loss.
-
Inflammation Reduction
Some peptides help control inflammation and support recovery after injury.
-
Skin Health
Peptides act as messengers that tell skin cells to make more collagen and elastin, two key proteins for firm, smooth, and radiant skin.
Key Areas of Modern Peptide Research
Modern peptide research is aiming to develop peptide-based therapeutics for various diseases, improve drug delivery systems, and use AI technology for new discoveries. Key research areas include:
-
Peptides in Skincare and Anti-Aging
Many skincare products now use peptides to help reduce fine lines and dryness. These small molecules can tell skin cells to make more collagen and elastin, two proteins that keep the skin firm and smooth. Studies show that certain peptides can improve skin texture and help wounds heal faster. Because they are small, peptides can move through the outer layer of skin better than many larger molecules.
-
Therapeutic Peptides in Medicine
In medicine, peptides are being used as new types of drugs. Some help manage conditions like diabetes, cancer, and infections. For example, insulin, which is a natural peptide, has long been used to help people with diabetes control their blood sugar. Now, scientists are designing new peptides that can target specific cancer cells or block harmful bacteria.
-
Peptides in Sports and Fitness
Athletes and fitness fans are also interested in peptides. Some peptides may help muscles recover faster or increase endurance by improving how cells repair themselves after training. According to some research, several trials are testing how peptide therapy might help with muscle loss or recovery from injury.
Note: Experts also warn that using unapproved peptide products can be risky, especially if they are not regulated by medical authorities such as the FDA.
Conclusion
Research continues to show that these tiny molecules can make a big difference. The more we learn about peptides, the better we understand how to use them safely and effectively. For researchers looking to explore these compounds further, ASN-LABS is a trusted peptides online store offering a wide selection of high-quality peptides. Every product of ours includes a Certificate of Analysis (COA), available upon request, to ensure quality and transparency. All products are intended solely for research and laboratory use, not for human consumption, medical use, or as dietary supplements.